-
Posts
437 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
3
Posts posted by united7170
-
-

Optiuni:
-Melt File
-Disable Windows Firewall
-UDB Spread
-Delay Ejecute
-Anti Virtual PC
-Restart Bot
Optiuni DDOS:
-HTTP
-TCP
-UDP
Optiuni Extras:
-Update | Inject File From URL ( Downloader )
-Temporizador De DDOs
-Restart Bot PC
-Shutdown Bot PC
-Restart Bot
-Icon Changer
-UPX
Download: Multiupload.nl - upload your files to multiple file hosting sites!
Pass : TTM=
-

- Extracts metadata from Open Office, MS Office, PDF, EPS and Graphic documents.
- Uses Google, Bing and Exalead to find and examine the following file types on a target website – doc, ppt, pps, xls, docx, pptx, ppsx, xlsx, sxw, sxc, sxi, odt, ods, odg, odp, pdf, wpd, svg, svgz, indd, rdp , and ica.
- From the extracted metadata, FOCA can find information on users, folders, printers, software, emails ,operating systems, passwords, servers and more.
- Network Discovery
- Fingerprinting
- DNS Cache Snooping
– discover what websites the internal users of a network are browsing on.
- Exports data into a Report
Download: Foca
pass: bGV2ZWwtMjMuYml6
-
CEHv7 provides a comprehensive ethical hacking and network security-training program to meet the standards of highly skilled security professionals. Hundreds of SMEs and authors have contributed towards the content presented in the CEHv7 courseware. Latest tools and exploits uncovered from the underground community are featured in the new package. Our researchers have invested thousands of man hours researching the latest trends and uncovering the covert techniques used by the underground community.
Content:

Download:
Size:
15.51GB
Pass:1nvalid
Source
-
In fiecare an, premiile EuroCloud aduc in prim plan cele mai inovatoare companii si business case-uri de cloud. Acestea beneficiaza de o mediatizare intensa atat in Romania cat si la nivel european si aduc sub lumina reflectoarelor cei mai buni candidati selectionati la nivel national.
Scopul acestei competitii este de a evidentia business case-urile inovatoare, performantele industriei de cloud si de a promova un climat competitional in cadrul industriei romanesti de cloud computing . Veti putea castiga unul din cele 4 premii EuroCloud Romania 2013 si va veti califica pentru a concura la Premiile EuroCloud Europa care se decerneaza in fiecare an in cadrul Congresului European EuroCloud.
Data limita de depunere a candidaturilor pentru premiile EuroCloud Romania este de 22 iulie 2013.
Categoriile de premii puse in competitie sunt:
- Cel mai bun start-up de cloud
- Cea mai buna oferta de cloud (SaaS, IaaS, PaaS)
- Cel mai bun proiect de cloud, sectorul public
- Cel mai bun proiect cloud, sectorul privat.
Cine poate candida?
Toate companiile romanesti sau cu o filiala deschisa in Romania, care au in oferta un serviciu de tip cloud (Saas, Iaas sau Paas) sau care au implementat proiecte cloud in mediul privat sau administratia publica romaneasca.
In cazul premiului “Cel mai bun start-up romanesc de cloud”, compania trebuie sa aiba sediul social in Romania si sa functioneze de mai putin de 2 ani.
Pentru premiile cel mai bun proiect de cloud, solutia trebuie sa fie folosita de o organizatie romaneasca sau de catre filiala sa stabilita in Romania.
De ce sa candidati ?
In fiecare an, premiile EuroCloud aduc in prim plan cele mai inovatoare companii si business case-uri de cloud. Acestea beneficiaza de o mediatizare intensa atat in Romania cat si la nivel european si aduc sub lumina reflectoarelor cei mai buni candidati selectionati la nivel national.
Candidaturile nominalizate de catre juriu vor fi publicate pe tot parcursul anului pe siteul EuroCloud Romania in sectiunea Premiile EuroCloud. Pe langa aceste avantaje, candidatii nominalizati isi vor putea prezenta solutiile in cadrul conferintei anuale a EuroCloud Romania, organizate la inceputul lunii octombrie 2013.
Castigatorii Premiilor EuroCloud Romania se vor pre-califica pentru a participa la Premiile EuroCloud Europa, care se vor decerna pe 15 octombrie 2013 in cadrul Congresului Anual EuroCloud Europa.
Cum candidati ?
Candidatii trebuie sa completeze un formular si sa puna la dispozitie o prezentare a solutiei proprii de cloud, care sa raspunda la o serie de criterii disponibile pe siteul EuroCloud Romania.
Care sunt criteriile ?
Aplicatiile vor fi evaluate in functie de mai multe criterii, aplicabile in functie de categoria de premii. Pentru a usura sarcina juriului, asigurati-va ca in descrierea serviciului de cloud din candidatura voastra mentionati modul in care solutia raspunde la aceste criterii:
-Calitate si profesionalism al candidaturii
-Creativitate si originalitate a serviciuluiFocus pe viitor, potential
-Perspective pentru acceptarea pe scara larga a serviciului in piata
-Functionalitati oferite
-Conectivitate si interoperabilitateUtilizare rationala a resurselor in datacenter
-Conformitate cu regulile de securitate a datelor, protectia datelor si compliance
-Nevoia de businessBeneficiul obtinut de catre client
-Avantaje competitive pentru clientBeneficiul obtinut in marketing / vanzari
-Nota personala a evaluatorului
Cine decide ?
EuroCloud Romania a reunit un juriu format din delegatii organizatiilor membre EuroCloud Romania, persoane recunoscute pentru experienta si angajamentul lor pentru cloud computing. Juriul va examina candidaturile depuse pana pe 22 iulie si vor delibera pana la sfarsitul lunii iulie pentru a decide cine vor fi castigatorii de anul acesta.
Nota: Membrii juriului nu vor putea vota asupra propriilor solutii sau proiecte trimise in competite.
Inscrieti-va acum la Premiile EuroCloud Romania 2013!
http://www.eurocloud.ro/prima-pagina/premiile-eurocloud-romania-2013/
Candidatura dv. la premiile EuroCloud Romania implica acceptarea Termenilor si Conditiilor. Pentru mai multe informatii si detalii, contactati secretariatul Premiilor EuroCloud Romania la email premii@eurocloud.ro. Asteptam candidaturile voastre si va dorim mult succes !
Despre EuroCloud Romania
EuroCloud Romania actioneaza ca o voce colectiva a industriei romanesti de cloud computing pentru a permite dezvoltarea unui ecosistem local de cloud, si a creste vizibilitatea pietei romanesti de cloud.
-
Infractorii cibernetici s-ar putea confrunta cu pedepse mai aspre la nivelul Uniunii Europene, conform noilor reguli adoptate de catre Parlamentul European, care includ crearea unei infractiuni distincte in ceea ce priveste utilizarea botnet.
Proiectul directivei adoptate de catre Parlamentul European defineste o serie de infractiuni in spatiul cibernetic si stabileste sanctiuni specifice pentru fiecare dintre acestea. De asemenea, solicita tarilor din Uniunea Europeana sa sprijine statele membre si sa raspunda la cererile urgente in termen de opt ore, in cazul producerii unui atac cibernetic.
Textul a fost deja aprobat, informal, de catre statele membre, acordul urmand sa fie formalizat in curand. Statele membre vor avea la dispozitie doi ani pentru a implementa acest acord la nivelul legislatiilor nationale.
Potrivit proiectului de lege, utilizarea botnet-urilor pentru a stabili controlul de la distanta asupa unui numar semnificativ de computere, prin infectarea acestora cu software rau intentionat, va fi sanctionata cu o pedeapsa de cel putin trei ani de inchisoare.
De asemenea, responsabilii pentru atacuri cibernetice impotriva "infrastructurii critice", cum ar fi centrale electrice, retele de transport si retele guvernamentale, se vor confrunta cu cel putin cinci ani de inchisoare. Aceeasi pedeapsa va fi aplicata in cazul in care un atac este derulat de catre o organizatie infractionala ori daca prin acesta se cauzeaza daune majore.
"Atacurile impotriva sistemelor informatice prezinta o provocare tot mai mare pentru companii, guverne si cetateni deopotriva. Astfel de atacuri pot cauza daune grave si slabesc increderea utilizatorilor in siguranta internetului", a declarat Comisarul pentru afaceri interne, Cecilia Malmstrom.
Companiile si organizatiile vor fi, de asemenea, raspunzatoare pentru infractiunile savarsite in beneficiul lor, cum ar fi, spre exemplu, angajarea unui hacker pentru a accesa baza de date a unui concurent.
Directiva, care actualizeaza regulile in vigoare incepand cu anul 2005, solicita, de asemenea, statelor membre, sa acorde judecatorilor posibilitatea de a condamna infractorii la doi ani de inchisoare pentru infractiunile constand in accesarea sau interferarea cu sistemele de informatii, interceptarea ilegala a comunicatiilor sau producerea si vanzarea instrumentelor utilizate pentru a savarsi astfel de infractiuni. Cazurile minore sunt exceptate, insa fiecare stat determina in ce consta astfel de cazuri.
Directiva se va aplica in toate statele membre ale Uniunii Europene, cu exceptia Danemarcei, care nu si-a manifestat acordul in acest sens.
-
A study of Google's and Mozilla's browser bug programs shows it is money well spent
Paying rewards to independent security researchers for finding software problems is a vastly better investment than hiring employees to do the same work, according to researchers from the University of California Berkeley.
Their study looked at vulnerability reward programs (VRPs) run by Google and Mozilla for the Chrome and Firefox web browsers.
Over the last three years, Google has paid US$580,000 in rewards, and Mozilla has paid $570,000. In the course of those programs, hundreds of vulnerabilities have been fixed in the widely used products.
The programs are very cost effective. Since a North American developer's salary will cost a company about $100,000 with a 50 percent overhead, "we see that the cost of either of these VRPs is comparable to the cost of just one member of the browser security team," the researchers wrote.
Additionally, more eyes on the code meant the VRPs uncovered many more software flaws than just one hired developer could find.
The study provides a sound foundation for reward programs, which are not embraced by all vendors. Adobe Systems and Oracle do not pay for vulnerability information.
Microsoft has traditionally not paid bounties, but did implement a one-off program last month. Through July 26, Microsoft will pay up to $11,000 for bugs in its Internet Explorer 11 browser.
Bug bounties have other advantages, such as by reducing the number of vulnerabilities that are sold to malicious actors who would use the information for criminal activity. The programs also make it harder for hackers to find vulnerabilities, the researchers wrote.
But a key difference between Google's and Mozilla's programs may affect their effectiveness.
Mozilla pays a flat $3,000 reward for a vulnerability. Google pays on a sliding scale, which ranges from $500 to $10,000. Google judges vulnerabilities and exploits on factors such as difficulty and impact.
Google's average payout is just $1,000, but the chance of obtaining a much higher reward appears to provide an incentive for more people to participate in its program, the researchers wrote.
Google's program, while costing about the same as Mozilla's, "has identified more than three times as many bugs, is more popular and shows similar participation from repeat and first-time participants."
"This makes sense with an understanding of incentives in lotteries: the larger the potential prize amount, the more willing participants are to accept a lower expected return, which, for VRPs, means the program can expect more participants," according to the paper.
Also, browser penetration contests such as "Pwnium" run by Google with rewards up to $150,000 sparks more interest among researchers.
-
sclipici, eu ma asteptam sa imi povestiti voi, ca eu nu am ce sa povestesc. de-aia am intrebat daca ati luat legatura cu aia de la mine de la scoala.
Da noi am fost. PA!
-
voi ati luat legatura cu lumea de la mine de la scoala?

Dude? Ce ai fumat ca vreau si eu.
-
You work hard to protect your PC from the malicious thugs of our digital world. You keep your antivirus program up to date. You avoid questionable Web sites. You don’t open suspicious email attachments. You keep Java, Flash, and Adobe Reader up-to-date—or better yet, you learn to live without them.
But against all odds, a clever new Trojan horse slipped through the cracks, and now you’re the unhappy owner of an infected PC. Or perhaps a less-vigilant friend has begged you to clean up a plague-ridden mess.
Obviously, you need to scan the computer and remove the malware. Here’s a methodical approach that you can use to determine what the problem is, how to scan, and what to do afterward to protect the PC from future invasions.
1. Verify the infection
Is the PC in question really infected? I’ve seen people blame “another damn virus” for everything from a bad sound card to their own stupidity. The first step in restoring the system’s health is to determine whether what you’re dealing with is a virus rather than a problem with hardware, software, or user error.
If your PC is unusually slow, or if it seems to do a lot of things on its own that you haven’t asked it to do, you have reason to be suspicious. But before you decide that a virus must be responsible, take a moment to launch the Windows Task Manager (right-click the Windows taskbar, and select Task Manager from the pop-up menu). Open the Processes tab, and check for any strange or unknown applications running in the background—especially those with nonsensical names and no recognizable authority listed in the description. The odd-looking “wuauclt” process is fine, for example, because it belongs to Microsoft (it’s actually part of the Windows Update service, as you can tell from the description.)
Of course, this is only general guidance; there's nothing to stop a piece of malware from masquerading as a legitimate process by sporting an inoffensive description. That said, you'd be surprised how often a piece of malware gives itself away with a line of strange characters or symbols where the process description should be.
2. Check for sure signs of malware
Truly insidious malware will preemptively block you from trying to remove it. If your PC suddenly won’t load utilities that might help you manually remove malware—such as msconfig or regedit—be suspicious. If your antivirus program suddenly stops loading, that’s a huge red flag.
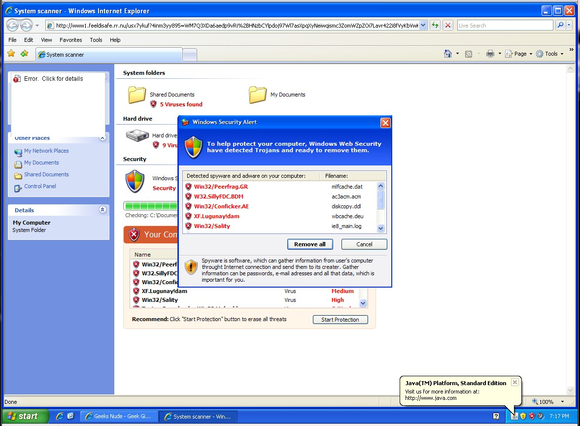
Fake warnings like this one try to scare you into running a file to 'remove malware' (read: install malware) or giving up your credit card information to pay for bogus antivirus software.
Sometimes the attack is more obvious. If a program you don’t recognize suddenly pops up and starts displaying dire warnings and asks you to run an executable file or asks for your credit card number, your PC is definitely infected with some nasty malware. Never fork over your credit card information or other personal data to a program or website that tries to warn you that your PC is about to die. More often than not it’s a rogue program, fear-mongering malware that tries to scare you into giving up your private info by issuing doomsday warnings of imminent hard drive failure, catastrophic viral infection, or worse.
3. Check online for possible fixes
The one benefit of those scary pop-ups is that they could point you toward a cure. Use your favorite search engine to look for phrases that appear in the pop-up—you’ll probably find other people fighting the same infection. Their experiences could help you identify your enemy or even find step-by-step instructions for removing the malware. Be prudent: Take advice only from sites that seem reputable, and remember to perform a full scan of your PC after you’ve followed any instructions, even ours.
Barring any clues that lead you to a magic solution, scanning becomes your next and most important step.
4. Assume that your old virus scanner is compromised
Don’t waste time scanning your hard drive(s) with your regular antivirus program. After all, that program probably failed to catch the malware in the first place.
But don’t be too hard on it. Nothing’s perfect, and even the best antivirus program can occasionally miss a new or particularly cleverly designed virus. And once that virus slips through, your antivirus program is compromised. You have to assume that the malware, not the security software, is in control.
You need a fresh malware scanner—one that’s not already installed on your computer. It must be capable of detecting and removing malware from your PC, and you need to run it in an environment where the malware can’t load first. Linux is your best bet, but before you jump to that option, try booting into Windows Safe Mode to see if you can outflank your virus infestation there.
5. Use a lightweight scanner inside Safe Mode
Windows has a Safe Mode that boots a minimal version of the operating system, with generic drivers and nothing else. It doesn’t load most startup applications and—most likely—it won’t load the malware that’s infesting your PC.
To enter Safe Mode, boot your computer and press the F8 function key before Windows starts loading. The timing is tricky, so it’s best to mash F8 repeatedly from the moment the motherboard manufacturer’s logo appears onscreen until you get the boot menu.
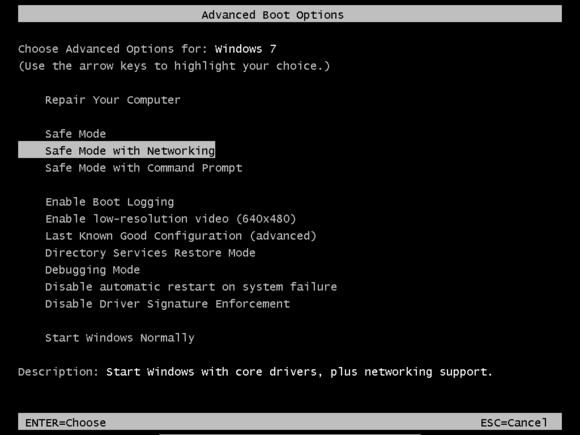
When you reach that menu, select Safe Mode with Networking from the list of boot options. The with Networking part is important—you’re going to need Internet access to solve your virus problem.
Once in Safe Mode, open Internet Explorer (using other browsers in Safe Mode is often problematic) and run a reputable online virus scanner such as Bitdefender. For best results I recommend using the ESET Online Scanner, a Web-based virus detection app that is always up-to-date and runs off a remote server. You’ll have to accept a browser add-in, but the scanner should remove it when it’s done. Before you start the scan, click Advanced settings and enable as many extra levels of scrutiny as you can, including scanning file archives and browser data.

The ESET Online Scanner runs in your browser and does a thorough job of rooting out malware from your PC.
You might also try Trend Micro’s HouseCall. Though it isn’t a Web app, it is portable, so you can download HouseCall on another computer and copy it to a flash drive, thereby creating a portable PC virus scanner. Then, when you run into trouble you can plug the flash drive into the infected PC and run the program from there (you’ll still need an Internet connection for a definition update, however.) When using HouseCall, don’t run it on default settings: Before you click the big blue Scan Now button, click Settings and select Full system scan.
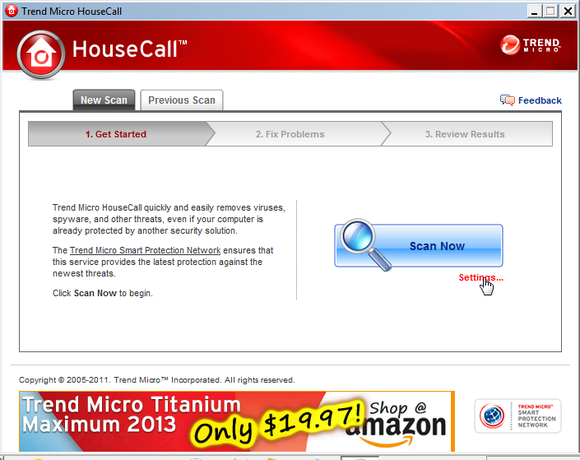
Trend Micro's HouseCall utility is another excellent, free virus scanner and malware removal tool.
Whichever scanner you use, don’t rush to get through this part of the process. Check the options and select the slowest, most thorough scan. Then, once the scan has started, step away from the PC. Read a book. Do the dishes. Spend time with someone you love. The scan will—and should—take hours.
6. Remember: The second scan's the charm
When that first scan is done—just to be sure—run another one with a different scanner. It’s easy, and you’ll sleep better after multiple scanners have assured you that your drive is clean.
7. Look to Linux as your last line of defense
Booting into Safe Mode may not short-circuit particularly malicious malware. If you still have trouble with an infection after running multiple scans in Safe Mode, you’ll have to bypass Windows altogether and avoid booting from the hard drive. To manage that trick, use a bootable CD or flash drive running a Linux-based antivirus utility.
You don’t have to know Linux to take this step. But you will want an Internet connection, since these scanners must go online to update their malware databases.
The first step is to download a bootable virus scanner as an .iso file. From it, you can easily create a bootable CD. In Windows 7, double-click the file and follow the prompts. In Windows 8, right-click the file and select Burn disc image. For earlier versions of Windows, you’ll need a third-party program such as the free ISO Recorder.
With its Windows-like user interface, the Kaspersky Rescue Disk will make you feel at home. But you have to be careful in setting up the scan. First, the Kaspersky Rescue Disk doesn’t update its malware dictionary automatically. To do this manually, select the Update Center tab and click Start update. Once the utility is updated, return to the Objects Scan tab, click Settings, and set the security level to the highest position. Make sure that all of your hard drives are checked before you start the scan and leave the room.
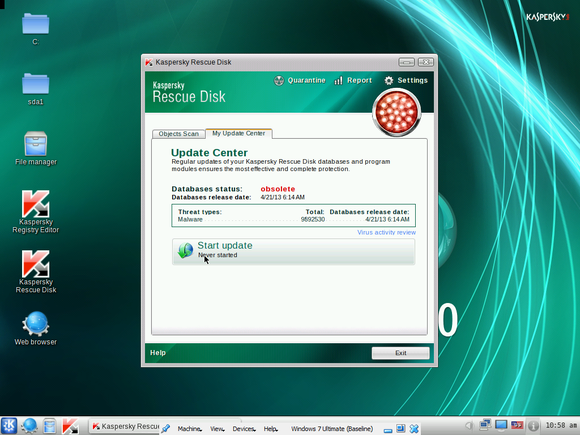
When you boot your PC with the Kaspersky Rescue Disk utility, you'll find yourself in a custom Linux environment. Simply update the Rescue Disk, crank all the scan settings up to maximum power, and let 'er rip.
If you want to boot the Kaspersky Rescue Disk from a flash drive, you’ll need to download the prosaically named Utility to record Kaspersky Rescue Disk 10 to USB devices. Save it in the same folder as the .iso file, run the utility, and follow the wizard.
The F-Secure Rescue CD isn’t as outwardly friendly as Kaspersky’s program. In fact, it may make you nostalgic for DOS. But it works, though you may receive the following (unduly alarming) warning message: If a Windows system file is infected, the computer may not restart. I’ve never heard of anyone whose Windows system failed to restart after an F-Secure scan, and I suspect that the eventuality is very rare. I also suspect that if malware did infect a Windows system file—and if F-Secure couldn’t clean the file without destroying it—reinstallation might be your only option anyway.
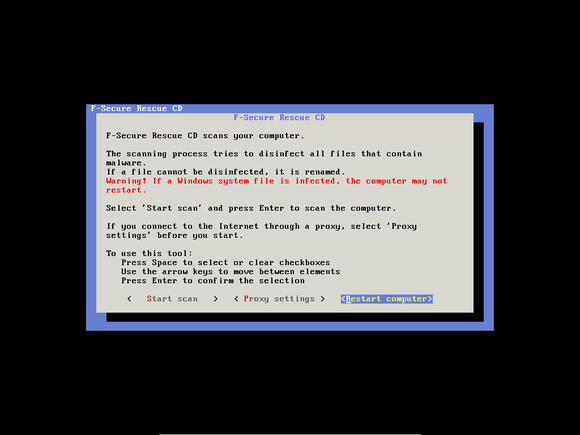
The F-Secure Rescue CD is a bare-bones cleaning utility for when you need to wipe every piece of malware from your PC without starting Windows.
F-Secure has a stripped down, unattractive, text-based user interface. But unlike Kaspersky, it updates its definitions automatically (if it can find an Internet connection), and starts a full, thorough scan with no fuss—you have to do little more than agree to the EULA.
F-Secure doesn’t offer a special USB utility. If you want to move a copy of it onto a flash drive, you’ll have to download and run the Universal USB Installer. In Step 1, you’ll find F-Secure Rescue CD near the bottom of a very long list. I suggest you go straight to the bottom, and then look for it while slowly scrolling up.
8. Protect your newly disinfected PC
When you’re satisfied that your drive is clean, try rebooting into good old Windows. Then uninstall your old antivirus program—it has been compromised.
Of course, you don’t want to stay unprotected. Reinstall the program and update to the latest version, or (if you’ve lost all faith in it) install a competitor. For more information on how to choose the best antivirus program for your needs, check out our full rundown—with empirical testing—of the best security software available today.
Because when it comes to malware, a byte of prevention is worth a terabyte of cure.
-
Color can evoke emotion, capture attention, and send a message. Whether you’re designing business cards, setting up a photo shoot, or shopping for throw pillows for your canary-yellow couch, choosing the right colors is important. Unless you’ve had a class in color theory, picking colors that go well together can be an exercise in frustration: Some colors pair up nicely, some don’t, and who the heck knows why? Here, I'll review a little color theory as well as how to choose colors using a gadget that dates back to the 17th century.
Color theory 101
A color scheme (or color palette) refers to the group of colors you use in a project, a painting, or your living room. Just take a look at any book cover, magazine ad, or website and you’ll see that it’s made from a certain set of colors. The designer usually picks a main color and then chooses the other colors according to how they look together and the feeling they evoke when they’re viewed as a group. There’s a whole science behind picking colors based on what they mean to us humans and how they make us feel, as shown in the image below. Those meanings and feelings can differ according to geographic location. For example, hospital rooms and public spaces are typically bathed in pale blue or green because those colors have a soothing effect, while a popular chain of truck stops (Loves) are swathed in bright yellow and red to keep drivers awake and alert, and Apple stores are predominantly white to reflect a feeling of elegance and simplicity.

When dealing with color, especially in software such as Photoshop Elements, you’re likely to encounter the following terms:
Hue is a term for pure color, before it’s had any white or black mixed with it. Pure color mixed with white is called a tint because it produces a lighter color than you had before (blue plus white equals light blue). Pure color mixed with black is called a shade and produces a darker color (blue plus black equals dark blue).
Saturation describes a color’s vibrancy. For example, a highly saturated hue has a vivid, intense color. A less saturated hue looks dull and gray. When picking colors that will appear side-by-side, it’s helpful to use similar saturation values.
Brightness determines how light or dark a color appears. You can think of brightness as the amount of light shining on an object, ranging from white (100 percent) to black (0 percent).
Using a color wheel
The simplest way to pick colors is to use a color wheel—a circular diagram of colors arranged by their relationships with one another. A color wheel is based on the three primary colors: yellow, blue, and red, from which all other colors spring. By mixing equal amounts of the primary colors, you get a second set of colors called secondary colors. Mixing equal parts of the secondary colors gives you a third set of colors called tertiary colors. Together, these colors comprise the color wheels shown here.

A typical color wheel is made from primary, secondary, and tertiary colors. While Sir Isaac Newton first arranged colors around a circular diagram in the late 1600s, one of the earliest known color wheels, dated 1708, is by the French painter Claude Boutet (it’s based on Newton’s diagram).
Using a color wheel is a two-step process: start by picking the main color you want the color scheme to revolve around—the colors in, say, a logo, a photo, or a canary-yellow couch—and then find the closest match to that color on the color wheel. Next, use one of the following color-scheme rules to identify where on the color wheel you should look to find other colors that go well with the first one.
Monochromatic schemes use colors from the same wedge of colors on the color wheel. Analogous schemes use colors from the wedges on both sides of the main color. Complementary schemes use colors from the wedge directly across from the main color.

There are numerous color-scheme rules, though these three are among the most practical and easiest to memorize. The main color in this scheme is blue, which came from the photo (marked by the red rectangle).
Most color wheels have a spinning-dial component that you use to point at your main color, and then a series of arrows that point you to associated color wedges for a particular color-scheme rule, as shown here.

A color wheel won’t turn you into the next Matisse, but for most mortals it’s the tool of choice for pairing colors. The one on the right has little windows that you can use to see how the colors you’re considering will look next to the real thing (say, a piece of fabric or spool of thread).
Using a color wheel is easy, once you get the hang of it. And when you do, you’ll be picking perfectly pleasing palettes in no time.
Linkuri utile:
Demonstration: Joseph Alber's Interaction of Color
Browse Palettes :: COLOURlovers
Color Combinations | Color Schemes | Color Palettes
https://kuler.adobe.com/create/color-wheel/
---> Sursa <---
-
Plm de distrusti, astea stiu ce inseamna ddos? Daca ei "pica" vreun site decent din cmd eu le dau cate 1k$ de persoana.
-
Pisam-as pe ea de limba romana. Nici Becali nu stia da asta nu l-a oprit sa se imbogateasca nu?
Nu invata ! Devino cioban ! Apoi sa te vad cum devii bogat.
Pisamas pe mentalitatea voastra de cacat!
ON: Dute in pana mea ie-ati o lada de bere 3 curve si lasa afaceriile. Totusi o "donatie" pentru un proiect ar fi buna dar proiectul respectiv trebuie gandit foarte bine pas cu pas. (avantaje-dezavantaje) .
-
@The Time : Ii putem sesiza usor pe cei care intra doar ca sa isi posteze linkurile cu ref.Topic-ul poate fi moderat de catre o anumita persoana care sa stea cu ochii la ce se posteaza.Apoi bineinteles ca vor exista restrictii.Cei cu sub 50 post-uri n-au voie.N-ai voie sa iti postezi toate link-urile in post-uri diferite ci toate intr-unul. Solutii exista de eliminare a spammerilor insa daca plecam cu negativism de prima data nu facem treaba.
//Structura unui post ar fi ceva de genul :
Denumire : xxx
Descriere : xxx si cu ce te ajuta pe tine ca iti intra cineva pe ref
Link : Ref : link direct fara alte site-uri si briz briz-uri
Daca ai mai multe site-uri de gen le postezi pe toate in acelasi post , unul sub altul de forma celui prezentat de mine.
De ce asi vrea eu sa dau click pe linkul tau de reff sau pe al altcuiva? Nu e destul offtopic? Trebuie sa vina si metinarii cu reff-links?
Sugestie inutila , propunere : T.C !

LE: Romanian Security Team(Center) , nu bazar cu linkuri de refferali !
-

Content:
Chapter 1 What Is SQL Injection?
1-Introduction
2-Understanding How Web Applications Work.
3-A Simple Application Architecture
4-A More Complex Architecture
5-Understanding SQL Injection
6-High-Profile Examples
7-Understanding How It Happens
8-Dynamic String Building
9-Incorrectly Handled Escape Characters
10-Incorrectly Handled Types
11-Incorrectly Handled Query Assembly
12-Incorrectly Handled Errors
13-Incorrectly Handled Multiple Submissions
14-Insecure Database Configuration
15-Summary
16-Solutions Fast Track
17-Frequently Asked Questions
Chapter 2 Testing for SQL Injection
1-Introduction
2-Finding SQL Injection
3-Testing by Inference
4-Identifying Data Entry
5-GET Requests
6-POST Requests
7-Other Injectable Data
8-Manipulating Parameters
9-Information Workf low
10-Database Errors
11-Commonly Displayed SQL Errors
12-Microsoft SQL Server Errors
13-MySQL Errors
14-Oracle Errors
15-Generic Errors
16-HTTP Code Errors
17-Different Response Sizes
18Blind Injection Detection
19-Confirming SQL Injection
20-Differentiating Numbers and Strings
21-Inline SQL Injection
22-Injecting Strings Inline
23-Injecting Numeric Values Inline
24-Terminating SQL Injection
25-Database Comment Syntax
26-Using Comments
27-Executing Multiple Statements
28-Time Delays
29-Automating SQL Injection Discovery
30-Tools for Automatically Finding SQL Injection
31-HP WebInspect
32-IBM Rational AppScan
33-HP Scrawlr
34-SQLiX
35-Paros Proxy
36-Summary
37-Solutions Fast Track
38-Frequently Asked Questions
Chapter 3 Reviewing Code for SQL Injection
1-Introduction
2-Reviewing Source Code for SQL Injection
3-Dangerous Coding Behaviors
4-Dangerous Functions
5-Following the Data
6-Following Data in PHP
7-Following Data in Java
8-Following Data in C#
9-Reviewing PL/SQL and T-SQL Code
10-Automated Source Code Review
11-Yet Another Source Code Analyzer
12-Pixy
13-AppCodeScan
14-LAPSE
15-Security Compass Web Application Analysis Tool (SWAAT)
16-Microsoft Source Code Analyzer for SQL Injection
17-Microsoft Code Analysis Tool .NET (CAT.NET)
18-Commercial Source Code Review Tools
19-Ounce
20-Source Code Analysis
21-CodeSecure
22-Summary
23-Solutions Fast Track
24-Frequently Asked Questions
Chapter 4 Exploiting SQL Injection
1-Introduction
2-Understanding Common Exploit Techniques
3-Using Stacked Queries
4-Identifying the Database
5-Non-Blind Fingerprint
6-Banner Grabbing
7-Blind Fingerprint
8-Extracting Data through UNION Statements
9-Matching Columns
10-Matching Data Types
11-Using Conditional Statements
12-Approach 1: Time-based
13-Approach 2: Error-based
14-Approach 3: Content-based
15-Working with Strings
16-Extending the Attack
17-Using Errors for SQL Injection
18-Error Messages in Oracle
19-Enumerating the Database Schema
20-SQL Server
21-MySQL
22-Oracle
23-Escalating Privileges
24-SQL Server
25-Privilege Escalation on Unpatched Servers
26-Oracle
27-Stealing the Password Hashes
28-SQL Server
29-MySQL
30-Oracle
31-Oracle Components
32-APEX
33-Oracle Internet Directory
34-Out-of-Band Communication
35-E-mail
36-Microsoft SQL Server
37-Oracle
38-HTTP/DNS
39-File System
40-SQL Server
41-MySQL
42-Oracle
43-Automating SQL Injection Exploitation
44-Sqlmap
45-Sqlmap Example
46-Bobcat
47-BSQL
48-Other Tools
49-Summary
50-Solutions Fast Track
51-Frequently Asked Questions
Chapter 5 Blind SQL Injection Exploitation
1-Introduction
2-Finding and Confirming Blind SQL Injection
3-Forcing Generic Errors
4-Injecting Queries with Side Effects
5-Spitting and Balancing
6-Common Blind SQL Injection Scenarios
7-Blind SQL Injection Techniques
8-Inference Techniques
9-Increasing the Complexity of Inference Techniques
10-Alternative Channel Techniques
11-Using Time-Based Techniques
12-Delaying Database Queries
13-MySQL Delays
14-Generic MySQL Bit-by-Bit Inference Exploits
15-SQL Server Delays
16-Generic SQL Server Binary Search Inference Exploits
17-Generic SQL Server Bit-by-Bit Inference Exploits
18-Oracle Delays
19-Time-Based Inference Considerations
20-Using Response-Based Techniques
21-MySQL Response Techniques
22-SQL Server Response Techniques
23-Oracle Response Techniques
24-Returning More Than One Bit of Information
25-Using Alternative Channels
26-Database Connections
27-DNS Exfiltration
28-E-mail Exfiltration
29-HTTP Exfiltration
30-Automating Blind SQL Injection Exploitation
31-Absinthe
32-BSQL Hacker
33-SQLBrute
34-Sqlninja
35-Squeeza
36-Summary
37-Solutions Fast Track
38-Frequently Asked Questions
Chapter 6 Exploiting the Operating System
1-Introduction
2-Accessing the File System
3-Reading Files
4-MySQL
5-Microsoft SQL Server
6-Oracle
7-Writing Files
8-MySQL
9-Microsoft SQL Server
10-Oracle
11-Executing Operating System Commands
12-Direct Execution
13-Oracle
14-DBMS_SCHEDULER
15-PL/SQL Native
16-Other Possibilities
17-Alter System Set Events
18-PL/SQL Native 9i
19-Buffer Overflows
20-Custom Application Code
21-MySQL
22-Microsoft SQL Server
23-Consolidating Access
24-Summary
25-Solutions Fast Track
26-Frequently Asked Questions
27-Endnotes
Chapter 7 Advanced Topics
1-Introduction
2-Evading Input Filters
3-Using Case Variation
4-Using SQL Comments
5-Using URL Encoding
6-Using Dynamic Query Execution
7-Using Null Bytes
8-Nesting Stripped Expressions
9-Exploiting Truncation
10-Bypassing Custom Filters
11-Using Non-Standard Entry Points
12-Exploiting Second-Order SQL Injection
13-Finding Second-Order Vulnerabilities
14-Using Hybrid Attacks
15-Leveraging Captured Data
16-Creating Cross-Site Scripting
17-Running Operating System Commands on Oracle
18-Exploiting Authenticated Vulnerabilities
19-Summary
20-Solutions Fast Track
21-Frequently Asked Questions
Chapter 8 Code-Level Defenses
1-Introduction
2-Using Parameterized Statements
3-Parameterized Statements in Java
4-Parameterized Statements in .NET (C#)
5-Parameterized Statements in PHP
6-Parameterized Statements in PL/SQL
7-Validating Input
8-Whitelisting
9-Blacklisting
10-Validating Input in Java
11-Validating Input in .NET
12-Validating Input in PHP
13-Encoding Output
14-Encoding to the Database
15-Encoding for Oracle
16-Oracle dbms_asser
17-Encoding for Microsoft SQL Server
18-Encoding for MySQL
19-Canonicalization
20-Canonicalization Approache
21-Working with Unicode
22-Designing to Avoid the Dangers of SQL Injection
23-Using Stored Procedures
24-Using Abstraction Layers
25-Handling Sensitive Data
26-Avoiding Obvious Object Names
27-Setting Up Database Honeypots
Chapter 9 Reference
1-Introduction
2-Structured Query Language (SQL) Primer
3-SQL Queries
4-SELECT Statement
5-UNION Operator
6-INSERT Statement
7-UPDATE Statement
8-DELETE Statement
9-*zensiert* Statement
10-CREATE TABLE Statement
11-ALTER TABLE Statement
12-GROUP BY Statement
13-ORDER BY Clause
14-Limiting the Result Set
15-SQL Injection Quick Reference
16-Identifying the Database Platform
17-Identifying the Database Platform via Time Delay Inference
18-Identifying the Database Platform via SQL Dialect Inference
19-Combining Multiple Rows into a Single Row
20-Microsoft SQL Server Cheat Sheet.
21-Blind SQL Injection Functions: Microsoft SQL Server
22-Microsoft SQL Server Privilege Escalation
23-OPENROWSET Reauthentication Attack
24-Attacking the Database Server: Microsoft SQL Server
25-System Command Execution via xp_cmdshell
26-xp_cmdshell Alternative
27-Cracking Database Passwords
28-Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Hashes
29-File Read/Write
30-MySQL Cheat Sheet
31-Enumerating Database Configuration Information and Schema
32-Blind SQL Injection Functions: MySQL
33-Attacking the Database Server: MySQL
34-System Command Execution
35-Cracking Database Passwords
36-Attacking the Database Directly
37-File Read/Write
38-Oracle Cheat Sheet
39-Enumerating Database Configuration Information and Schema
40-Blind SQL Injection Functions: Oracle
41-Attacking the Database Server: Oracle
42-Command Execution
43-Reading Local Files
44-Reading Local Files (PL/SQL Injection Only)
45-Writing Local Files (PL/SQL Injection Only)
46-Cracking Database Passwords
47-Bypassing Input Validation Filters
48-Quote Filters
49-HTTP Encoding
50-Troubleshooting SQL Injection Attacks
51-SQL Injection on Other Platforms
52-PostgreSQL Cheat Sheet
53-Enumerating Database Configuration Information and Schema
54-Blind SQL Injection Functions: PostgreSQL
55-Attacking the Database Server: PostgreSQL
56-System Command Executio
57-Local File Access
58-Cracking Database Passwords
59-DB2 Cheat Sheet
60-Enumerating Database Configuration Information and Schema
61-Blind SQL Injection Functions: DB2
62-Informix Cheat Sheet
63-Enumerating Database Configuration Information and Schema
64-Blind SQL Injection Functions: Informix
65-Ingres Cheat Sheet
66-Enumerating Database Configuration Information and Schema
67-Blind SQL Injection Functions: Ingres
68-Microsoft Access
69-Resources
70-SQL Injection White Papers
71-SQL Injection Cheat Sheets
72-SQL Injection Exploit Tools
73-Password Cracking Tools
74-Solutions Fast TrackDownload: GirlShare - Download SQLI.rar
pass: rstcenter
-
-
Cei din clip sunt doar niste protestatanti...
 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_qNE5l8vzNM
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_qNE5l8vzNMAltele:
Exista multi oameni buni la suflet carora le place sa daruiasca celor care nu au. Dar din pacate in Romania si de ai vrea sa daruiesti, nu ai cui. Tiganii nu merita un astfel de tratament , ei sunt niste paduchi pentru omenire.
-
Decideti voi cat de folositoare va sunt tutorialele. Mie mi-au "cazut" chiar bine, unele
 .
.Torents :
The Pirate Bay - The galaxy's most resilient bittorrent site
http://filelist.ro/browse.php?search=lynda&cat=0&searchin=0&sort=0
PHP First Look:
GirlShare - Download Lynda.PHP.5.5.First.Look.TUTORiAL-ALTAiR.rar
0. http://filelist.ro/details.php?id=234393
1. http://filelist.ro/details.php?id=235644
2. http://filelist.ro/details.php?id=236410
3. http://filelist.ro/details.php?id=236781
4. http://filelist.ro/details.php?id=236782
5. http://filelist.ro/details.php?id=236892
6. http://filelist.ro/details.php?id=236893
7. http://filelist.ro/details.php?id=237322
8. http://filelist.ro/details.php?id=237323
9. http://filelist.ro/details.php?id=237325
-
-
Nu stiu de ce ma obosesc sa le raspund la prosti :
@xp2009 Esti sigur?
@XoddX esti un idiot! Cum mortii matii vrei sa fie un pack cu raturi si keyloggere ? Clean ?
@de2apandi what password dude ?

-
si ce legatura are cu ce am zis
 ? si cum iti dai seama ca n-am invatat nimic?
? si cum iti dai seama ca n-am invatat nimic?Ce legatura are?
Ce modalitate imi recomandati pentru a face bani dar fara a plati prea mult maxim 10-12$ as vrea sa platesc si cat mai rar.Ti-am enumerat o lista de "joburi" sa le zicem asa , din care poti scoate un banut .
Tu vrei sa devii milionar cu 10$ ?
P.S Imi dau seama ca nu ai invatat nimic dupa ultimele tale 10 posturi numai in sectiunea ajutor si cereri.
-
dorm eu si nu stiam?
Esti din 2012 aici si nu ai invatat nimic.
- Webdesign
- Webscripting
- Programare
- SEO si alte cacaturi

- Domeniu + host + o nisa buna
- Webchat ( iti bagi telecomanda in fund si iei bani)
si multe altele....
-
Sa tinem un moment de reculegere si sa ne amintim ce a zis un om batran. (nu mai stiu cine
 )
)"Nu mai faceti in p*la mea trade-uri cu romanii, sunt in stare sa iti dea in cap pentru 10 lei." (faceti trade-uri cu ei numai daca sunteti siguri 100% ca nu va luati teapa)
-
De ce nu inveti sa ti le faci singur?

Incearca cu proxy goblin sau tor (ceapa).
-
Ce ai ma cu garda? Nu te-au lasat sa iti rulezi jointul la colt de bloc?
Bun venit , arunca o privire peste regulament





Salutare
in Bine ai venit
Posted
Brasovean de-al meu Bun venit !
Bun venit !